Introduction
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) shipping is a critical Incoterm for businesses engaged in international trade, particularly for exporters in China shipping to Saudi Arabia. Under DDP terms, the seller assumes full responsibility for delivering goods to the buyer’s specified location, including all costs and risks associated with transportation, customs clearance, and import duties. This guide provides a detailed overview of DDP shipping from China to Saudi Arabia, covering its definition, costs, processes, benefits, challenges, and practical tips for both sellers and buyers, based on research from various logistics sources as of July 18, 2025.
1. Definition and Explanation of DDP
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) is one of the 11 Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) defined by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). Under DDP terms, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the buyer’s designated location, cleared for import. This means the seller must handle:
- Export Clearance: Ensuring all export documentation and procedures in China are completed.
- International Transportation: Arranging and paying for shipping, whether by sea or air.
- Import Clearance: Managing customs procedures in Saudi Arabia, including paying import duties, taxes, and fees.
- Final Delivery: Transporting the goods to the buyer’s specified address.
In practical terms, DDP means the seller delivers the goods when they are placed at the disposal of the buyer, cleared for import at the named place of destination. This is particularly advantageous for buyers in Saudi Arabia, as it simplifies the import process and ensures compliance with local regulations. However, it places significant responsibility on the seller, who must manage all logistics and bear all associated costs.
2. Benefits of DDP Shipping
DDP shipping offers distinct advantages for both sellers and buyers, as highlighted in sources like Dantful and Basenton:
- For Sellers:
- Increased Control: By managing the entire shipping process, sellers can ensure that their goods are handled properly and that all documentation is correct, reducing the risk of delays or rejections.
- Potential for Higher Profit Margins: Sellers can incorporate shipping costs into the product price, allowing for better pricing strategies and potentially higher margins.
- For Buyers:
- Simplified Process: Buyers do not need to deal with customs clearance or pay import duties separately; everything is handled by the seller, reducing administrative burden.
- Reduced Risk: Since the seller is responsible for all aspects of delivery, buyers are protected from potential issues like incorrect documentation, unpaid duties, or delays.
- No Hidden Costs: The total price quoted by the seller includes all shipping, duties, and taxes, ensuring transparency and avoiding surprises upon delivery.
3. Costs of DDP Shipping
The cost of DDP shipping from China to Saudi Arabia can vary depending on several factors, including the type and volume of goods, the mode of transportation (air or sea), and seasonal demand. Based on data from Dantful and DDPCH, here’s a breakdown of typical cost components:
- Shipping Charges:
- Sea Freight: Approximately $2,000 for a 20ft container; $2,500 for a 40ft container, based on routes from Shanghai or Shenzhen to Jeddah or Dammam.
- Air Freight: Around $5 per kg for shipments over 1,000 kg; smaller shipments may cost $5–$8 per kg, depending on the forwarder and urgency.
- Customs Duties and Taxes:
- Saudi Arabia imposes a 15% VAT on the CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) value of imports.
- Customs duties range from 5% to 20%, depending on the product type (e.g., electronics: 5–20%, textiles: 12%, machinery: 5–15%).
- Insurance:
- Typically 1–2% of the goods’ value, to cover potential losses or damages during transit.
- Handling Fees:
- Includes warehouse handling, documentation, and other service fees, ranging from $100 to $500, depending on the complexity of the shipment.
Example Cost: For consumer electronics shipped via air freight (1,000 kg), the total DDP cost might be approximately $2,600, including:
- Shipping: $5,000
- Customs Duties and Taxes: $800
- Insurance: $200
- Handling Fees: $100
Factors Affecting Costs:
- Type and Volume of Goods: Larger or heavier shipments may qualify for better rates, while specialized goods (e.g., refrigerated containers) may incur additional fees.
- Transportation Mode: Air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight, suitable for urgent or high-value goods.
- Seasonal Demand: July is a peak season due to post-Hajj demand, which can increase rates and lead to capacity constraints.
- Geopolitical Events: Red Sea disruptions may indirectly affect costs by increasing overall logistics expenses, though DDP sellers must absorb these costs.
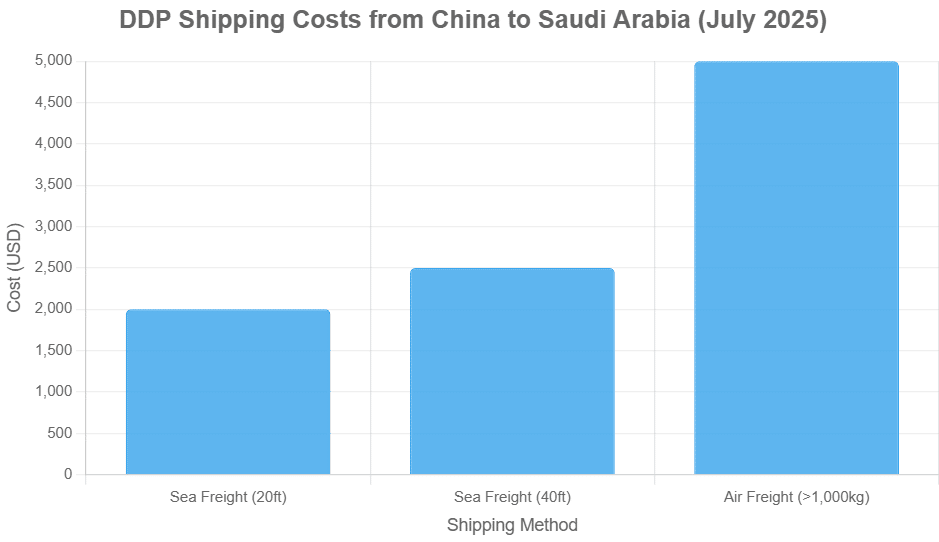
Table: Estimated DDP Shipping Costs from China to Saudi Arabia (July 2025)
| Shipping Method | Container/Weight | Cost (USD) | Transit Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Freight (FCL) | 20ft Container | $2,000 | 20–40 days |
| Sea Freight (FCL) | 40ft Container | $2,500 | 20–40 days |
| Air Freight | >1,000 kg | $5,000 (1,000 kg) | 3–5 days |
Note: Costs are approximate and may vary based on specific goods, routes, and market conditions. Always consult freight forwarders for precise quotes.
4. Shipping Methods Under DDP
DDP shipping can be executed via sea freight or air freight, depending on the urgency and nature of the goods, as detailed in sources like ChinaDdpShipping.Com and DDPCH:
- Sea Freight:
- Cost: Generally lower, suitable for large volumes or less time-sensitive goods, with costs around $2,000–$2,500 for 20ft and 40ft containers.
- Transit Time: 20–40 days, depending on the route (e.g., Shanghai to Jeddah: 25–35 days).
- Key Ports:
- China: Shanghai, Shenzhen, Ningbo.
- Saudi Arabia: Jeddah Islamic Port, King Abdulaziz Port (Dammam).
- Air Freight:
- Cost: Higher, around $5 per kg for shipments over 1,000 kg; smaller shipments may cost $5–$8 per kg.
- Transit Time: 3–5 days, including flight time (approximately 6.5 hours) and handling.
- Key Airports:
- China: Shenzhen Bao’an, Shanghai Pudong, Beijing Capital.
- Saudi Arabia: King Fahd International (Dammam), King Abdulaziz International (Jeddah), King Khalid International (Riyadh).
Comparison:
- Sea Freight: Ideal for bulk, non-urgent shipments due to lower costs, but slower, making it unsuitable for time-sensitive goods.
- Air Freight: Best for urgent, high-value, or perishable goods due to speed, though significantly more expensive.
5. Documentation and Compliance
Under DDP terms, the seller must ensure all necessary documentation is prepared and submitted correctly, as outlined in Dantful’s article. Key documents include:
- Commercial Invoice: Details the goods, their value, and the parties involved, serving as proof of transaction.
- Packing List: Lists the contents of each package, ensuring transparency for customs.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill: Issued by the shipping line or airline, acting as a receipt and contract for the shipment.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for certain goods to qualify for tariff exemptions or comply with trade agreements, potentially reducing customs duties.
- Import Licenses and Permits: Necessary for restricted or regulated goods, such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, or agricultural products, to ensure compliance with Saudi standards.
Compliance with Saudi Arabian Regulations:
- Prohibited Items: Alcohol, pork, weapons, explosives, pornographic materials, gambling equipment, and certain religious artifacts are banned.
- Restricted Items: Agricultural seeds, live animals, books, periodicals, chemicals, and wireless devices may require special permits. Check the latest restricted item lists via the Saudi Customs Service.
- Customs Duties and VAT: Sellers must pay a 15% VAT and customs duties ranging from 5% to 20%, depending on the product type (e.g., electronics: 5–20%, textiles: 12%).
Tip: Use tools like Freightos for cost estimation and SimplyDuty for duty calculations to ensure accuracy.
6. Logistics and Delivery
The DDP process involves the following steps, as detailed in sources like ChinaDdpShipping.Com:
- Seller Arranges Carriage and Export Clearance:
- Goods are prepared, packed, and cleared for export from China. The seller’s factory cannot be the exporter; a freight forwarder typically handles this.
- Seller Pays Import Duties and Taxes:
- Upon arrival in Saudi Arabia, the seller manages customs clearance and pays all duties, taxes, and fees, ensuring the goods are released for import.
- Buyer Receives and Unloads Goods:
- The seller delivers the goods to the buyer’s specified location, such as Amazon FBA warehouses, business addresses, or private addresses, where the buyer unloads them.
Key Considerations:
- Export Declaration: The seller must use a freight forwarder or logistics provider for export declaration, as factories cannot declare directly.
- Destination Flexibility: DDP allows delivery to various locations, including Amazon FBA warehouses, enhancing convenience for e-commerce sellers.
7. Challenges and Considerations
While DDP offers many benefits, it also presents challenges, as noted in Dantful’s article:
- Higher Upfront Costs for Sellers: Sellers bear all costs, which can be significant, especially for air freight or high-duty goods, potentially impacting cash flow.
- Logistics Complexity: Managing the entire shipping process requires expertise and resources, including handling customs clearance in a foreign country like Saudi Arabia.
- Dependence on Seller: Buyers rely entirely on the seller for timely and correct delivery, which can be risky if the seller lacks experience or faces logistical issues.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Effective Communication: Regular updates between seller and buyer can prevent misunderstandings and ensure alignment on delivery expectations.
- Reliable Freight Forwarders: Partner with experienced forwarders like ChinaDdpShipping.Com or DDPCH for smooth operations and compliance.
- Tracking Technology: Use real-time tracking systems provided by forwarders to monitor shipments and address issues promptly, enhancing transparency.
8. Practical Tips
- For Sellers:
- Ensure all documentation is accurate and complete to avoid delays, as incomplete paperwork can lead to customs holds and additional costs.
- Stay updated on Saudi Arabian customs regulations and any changes, such as the upcoming ban on letters of commitment for clearance starting January 1, 2026.
- Consider insurance to cover potential losses or damages during transit, especially for high-value goods.
- For Buyers:
- Clearly specify the delivery address and any special requirements, such as temperature-controlled storage for perishables.
- Verify the seller’s reliability and experience with DDP shipments, checking reviews or past performance with forwarders like Basenton.
- Understand the total cost, including all duties and taxes, to avoid surprises, using tools like Freightos for estimates.
9. Conclusion
DDP shipping from China to Saudi Arabia is a streamlined and convenient solution for international trade, offering simplicity for buyers and control for sellers. By understanding the costs, processes, and benefits of DDP, both parties can navigate the complexities of global shipping more effectively. With proper planning, reliable partners, and attention to compliance, DDP can facilitate smoother transactions and stronger business relationships between China and Saudi Arabia as of July 18, 2025.


