Introduction: Why China to USA Shipping Routes Matter in Global Trade
China to USA shipping routes are the backbone of international trade. As the two largest economies in the world, the volume of goods exchanged daily between China and the United States is enormous — from electronics and textiles to automotive parts and industrial equipment. These shipping routes not only define how long it takes to ship from China to the US, but also impact shipping costs, delivery reliability, and global supply chain performance.
Whether you’re shipping by sea, air, or a mix of both, understanding the shipping routes from China to the USA, including main ports, distances, and transit times, is crucial for business success in 2025.
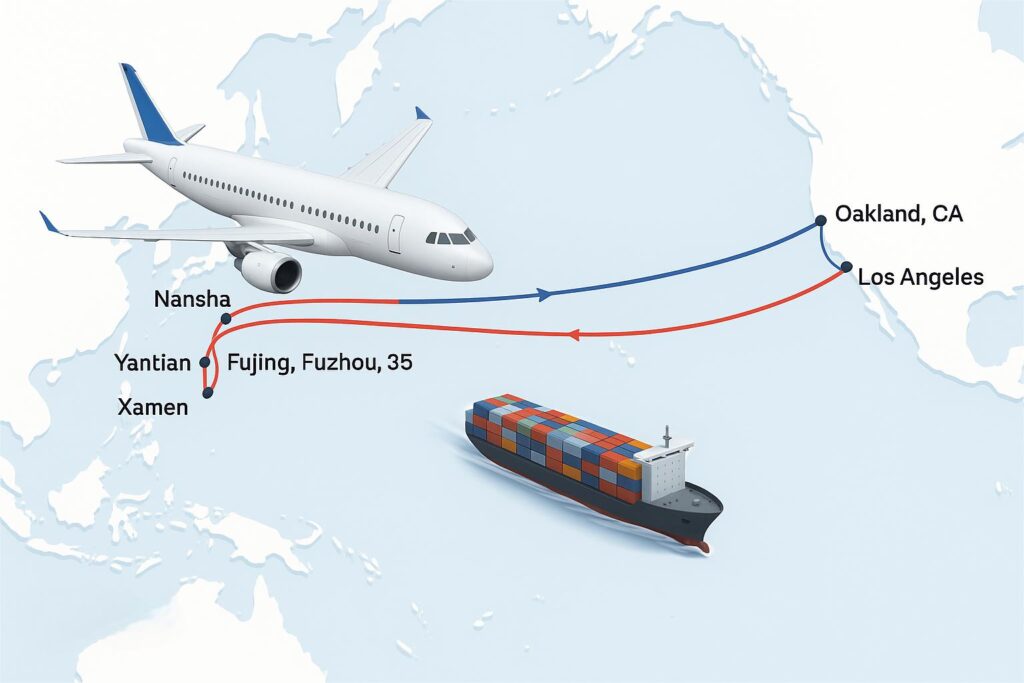
Major Sea Shipping Routes from China to the USA
In global trade, sea shipping is the preferred method for transporting large volumes of goods due to its cost effectiveness and extensive reach. The strategic sea routes from China to the USA primarily traverse the vast Pacific Ocean, connecting major Chinese ports with key American harbors. Understanding these routes is fundamental to grasping usa sea route distance, transit time, and overall freight costs.
The Pacific Route – Backbone of Sea Shipping
The Pacific route remains the most common path for vessels leaving major Chinese ports such as Shanghai, Ningbo, and Shenzhen. This route offers a direct and efficient pathway:
Distance & Transit Time: With a typical journey of thousands of nautical miles, the transit time depends on vessel speed and port congestion. Generally, shipping from China to the US West Coast takes around 14–18 days.
Cost Considerations: Lower fuel costs and economies of scale make the Pacific route attractive, though fluctuating demand and port fees may affect overall shipping cost.
The Role of the Panama Canal in Shipping Routes
An alternative to the direct Pacific route is the Panama Canal route:
Key Benefits: Vessels targeting the US East Coast may benefit by transiting through the Panama Canal. This route, despite a slightly longer distance, offers direct access to ports like New York and Savannah.
Freight Costs & Efficiency: Although passing through the canal comes with associated tolls, the strategic reduction in distance compared to alternative circumnavigations can reduce overall costs when optimizing freight forwarder pricing strategies.
Dealing with Port Congestion and Other Challenges
A critical factor in sea shipping routes is the potential for port congestion:
Impact on Transit Time: Major ports such as Los Angeles, Long Beach, and New York often experience delays due to high cargo volumes. Such congestion can extend the estimated transit time.
Optimizing Routes: To avoid delays, shippers may choose less congested ports or alternative routes, ensuring more predictable shipping schedules, especially when calculating the usa sea route distance and overall delivery reliability.
Comparing Sea Routes – Direct vs. Alternative Paths
Shippers must decide between direct routes and alternative shipping paths:
Direct Routes: Vessels sailing directly through the Pacific generally offer faster transit time, ideal for time-sensitive cargo.
Alternative Routes: For destinations on the East Coast, the Panama Canal route represents an effective alternative, balancing route distance with overall shipping efficiency.
Air Freight Routes from China to the USA
For time-sensitive shipments, air freight from China to the USA offers the fastest delivery method. While more expensive than sea freight, air cargo is essential for electronics, medical equipment, perishable goods, and high-value items. Understanding the flight route from China to the USA, key airports, and average transit times helps shippers make informed decisions when balancing cost and urgency.
Key China to USA Air Freight Routes
Several direct and indirect air freight routes connect major Chinese airports with key U.S. destinations. The most commonly used airports include:
In China: Beijing Capital (PEK), Shanghai Pudong (PVG), Guangzhou Baiyun (CAN), and Shenzhen Bao’an (SZX)
In the USA: Los Angeles (LAX), Chicago O’Hare (ORD), New York (JFK), and Dallas/Fort Worth (DFW)
Most international flights follow the north pacific route, passing over northeast China, Alaska, and the northwest of the United States, before descending to inland or coastal destinations.
Transit Time and Flight Distance
Air shipping is ideal when transit time is a priority:
Typical Flight Duration: Direct flights from Shanghai to Los Angeles or Chicago take around 12–14 hours.
Flight Distance: The average distance from China to the USA by air ranges between 6,000 to 7,500 miles, depending on origin and destination airports.
How Long Does Shipping Take: Including customs clearance, total delivery time ranges from 3 to 7 days, making it significantly faster than any sea route.
Air Freight Cost Considerations
Air freight rates are calculated based on chargeable weight, which considers both actual and volumetric weight. Costs vary by season, cargo type, and airline capacity. Although air freight is more costly than sea freight, its speed and reliability often justify the expense, especially for international shipping with tight delivery deadlines.
Popular Airlines & Logistics Carriers
Major airlines that operate cargo flights from China to the USA include:
China Eastern, Air China Cargo, Cathay Pacific, and SF Airlines on the Chinese side.
FedEx, UPS, DHL Aviation, and Northwest Airlines Beijing (for transpacific partnerships) on the American side.
Many freight forwarders also provide door-to-door air freight services, combining customs clearance and final-mile delivery.
Key Chinese Ports and U.S. Destination Ports
Understanding the origin and destination ports along the China–USA shipping route is essential for planning logistics, managing transit time, and estimating overall freight costs. Each port offers unique advantages based on location, infrastructure, and connectivity to strategic shipping routes China utilizes.
Major Chinese Ports for Exports to the USA
China’s export network is anchored by several high-capacity ports located along its eastern coastline:
Port of Shanghai: The world’s busiest container port, offering direct access to the Pacific route and capable of handling both bulk and container loads efficiently.
Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan: Known for its deep-water access and rapid throughput, this port serves much of China’s industrial east.
Port of Shenzhen: Ideal for exports from Guangdong Province and South China, with strong connections to South China Sea and global shipping lanes.
Port of Qingdao, Xiamen, and Tianjin: Secondary ports that support additional export volume and offer more flexible departure schedules.
These major Chinese ports connect to multiple shipping routes China considers strategic, offering both direct and indirect sailings to the U.S.
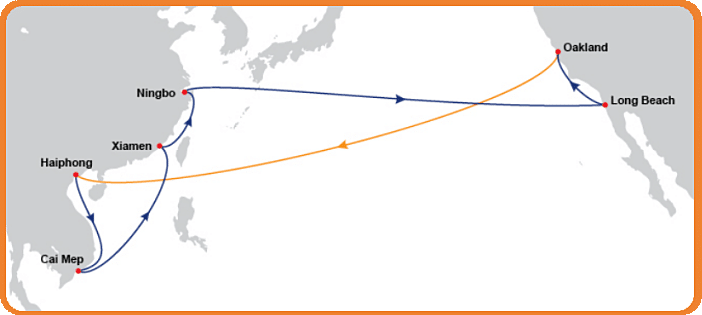
U.S. West Coast Ports – Primary Entry for Pacific Route
Most sea freight from China enters through the U.S. West Coast, thanks to its proximity across the Pacific Ocean:
Port of Los Angeles: The largest port in the United States, handling more than 20% of all U.S. imports. It offers direct access to California’s logistics infrastructure and is a critical destination port on the Pacific corridor.
Port of Long Beach: Located adjacent to LA, it works in tandem to process large volumes of Asia–U.S. cargo. It often serves as an alternative when port congestion occurs at LA.
Port of Oakland and Seattle: Secondary ports with growing importance for importers seeking faster inland access or avoiding Southern California congestion.
These West Coast ports are ideal for shipments using the north pacific route and offer shorter transit times from China.
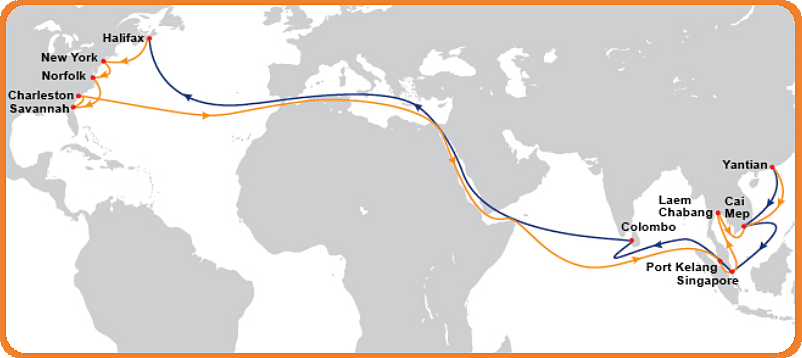
U.S. East Coast and Gulf Coast Ports
While less common than West Coast arrivals, many importers prefer shipping directly to the East or Gulf Coasts using longer routes via the Panama Canal or Suez Canal route:
East Coast Ports: New York/New Jersey, Savannah, and Charleston offer access to major markets on the East Coast and are becoming increasingly popular due to port congestion on the West Coast.
Gulf Coast Ports: Houston and New Orleans handle growing volumes of cargo, especially for shipments originating in South China or routed via the Indian Ocean.
These ports increase flexibility for cargo headed inland or toward South America, the Atlantic route, or even Western Europe.

Transit Times and Sea Route Distances from China to the USA
One of the most frequently asked questions in international logistics is:
“How far is China from the USA, and how long does shipping take?”
Whether you choose sea or air freight, understanding these metrics is essential for setting delivery expectations and optimizing your supply chain.
How Far is China from the United States by Sea?
The sea route distance between China and the USA varies based on origin and destination ports:
Shanghai to Los Angeles: ~6,000 nautical miles
Shenzhen to Long Beach: ~6,200 nautical miles
Ningbo to New York (via Panama Canal): ~11,000 nautical miles
These figures represent the initial sea journey, excluding possible delays or transshipment stops. The usa sea route distance increases significantly for East Coast and Gulf Coast destinations due to longer navigation paths through the Panama Canal or Suez Canal route.
How Long Does Shipping Take from China to the US?
Sea Freight Transit Times (based on direct routes):
To West Coast ports: 14–18 days
To East Coast ports: 25–35 days
To Gulf Coast ports: 28–38 days
These estimates may vary due to port congestion, customs clearance time, and weather conditions. When calculating delivery windows, it’s important to factor in transit time, container loading, and inland transportation.
Air Freight Transit Time and Distance
Air shipping is significantly faster:
Flight time from major Chinese cities (Shanghai, Beijing, Guangzhou) to U.S. cities (LAX, JFK, ORD): ~12–15 hours
Total delivery time, including ground handling and customs clearance: 3–7 days
In terms of flight route distance, the typical China to USA flight route spans between 6,000 and 7,500 miles, depending on airports and airspace paths.
Direct Routes vs. Extended Paths
Shipping companies may choose between direct routes and longer but strategically optimized ones:
Direct Routes: Across the Pacific Ocean, minimizing distance and transit time
Extended Routes: Through the Panama Canal or Suez Canal, often necessary for East Coast or European-bound cargo
Selecting the right path depends on the destination port, urgency, and freight category.
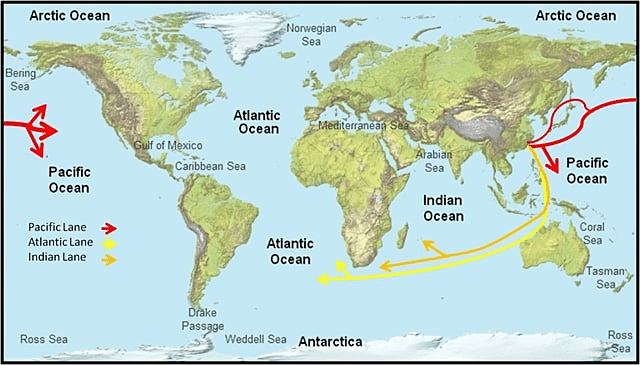
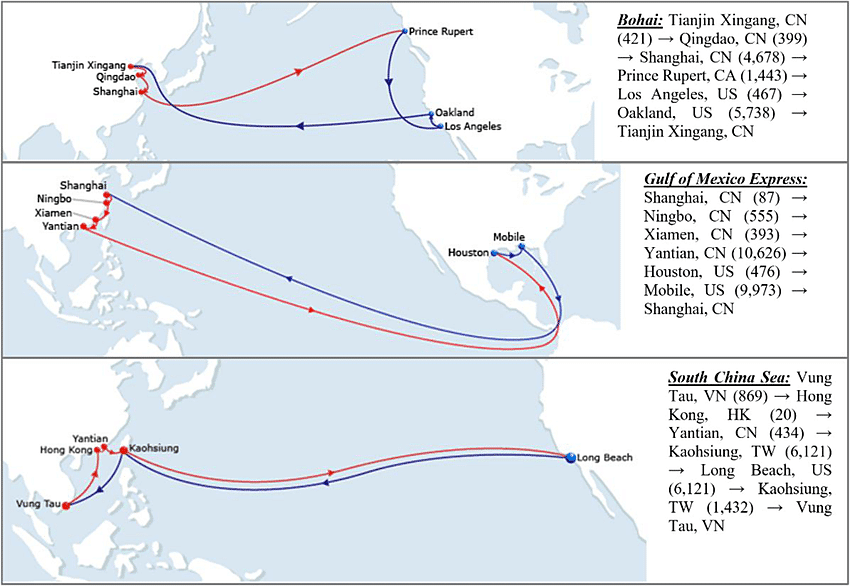
Shipping Route Maps – Visualizing Paths from China to the USA
To better understand how goods move across the globe, logistics planners and businesses often rely on shipping route maps to identify the most effective paths from China to the United States. These maps highlight major shipping lanes, chokepoints, and potential rerouting areas, providing a bird’s-eye view of global cargo traffic.
Common Sea Shipping Routes from China to the USA
Most cargo vessels departing from Chinese ports follow well-established shipping routes from China to USA, crossing the Pacific Ocean to reach North America. There are three primary visual routes represented on shipping maps:
Direct Pacific Route – Shanghai/Ningbo/Shenzhen to Los Angeles/Long Beach
Fastest route on the map
Avoids canal fees
Most common shipping route
Panama Canal Route – For East Coast-bound cargo
From China to Panama, then up to ports like New York, Savannah, or Miami
Shipping routes China uses to access the Atlantic side of the U.S.
Suez Canal and Indian Ocean Route – Rare, but used for global cross-shipping
From South China across the Indian Ocean, through Suez Canal, and toward Europe or East Coast USA
Longer, but strategic in certain trade setups
Shipping Routes Map Highlights
Key elements found on modern cargo shipping route maps include:
Map from China to USA showing estimated sea distances and transit times
Shipping routes China to US with color-coded paths (direct vs. canal-based)
Visualization of port congestion areas, especially around Los Angeles and Long Beach
Arrows or dotted lines indicating freight shipping routes and their intensity levels
These visuals help freight forwarders and importers optimize shipping paths, anticipate delays, and evaluate alternative ports.
Cargo and Air Freight Maps
Besides sea routes, air freight maps highlight major China to USA flight routes, typically moving over the North Pacific, with direct connections between Beijing, Shanghai, and U.S. hubs like Chicago, Los Angeles, and New York.
For larger supply chains, combined shipping maps (sea + land + air) illustrate sea and land transport flows — a valuable resource for businesses using multimodal shipping services.
Learn more:
20FT & 40FT Container Shipping Rates from China to USA
20ft & 40ft Container Shipping Costs from Taiwan to the USA
Does Taobao Ship to the USA? How to Buy and Ship from China
Shipping Cost from China to the USA (2025 Guide)
How to Reduce Import Duty When Shipping from China to the USA
DDP Shipping from China to USA: Air & Sea Freight Cost and Delivery Time (2025 Guide)
Factors Affecting Route Choice and Shipping Time
Choosing the best shipping route from China to the USA isn’t just about distance — it’s a strategic decision that balances shipping cost, transit time, and port conditions. For importers and logistics professionals, understanding what affects route efficiency can lead to smarter, faster, and more cost-effective supply chain decisions.
Freight Costs and Container Load Types
One of the most critical factors is freight cost, which varies depending on:
Container Load: Full Container Load (FCL) vs. Less than Container Load (LCL)
Shipping Method: Standard sea freight, express air freight, or multimodal transport
Peak Season Surcharges: Demand spikes lead to elevated prices
For example, FCL offers better cost-per-unit rates but may not suit small shipments. LCL is more flexible but involves longer transit time due to cargo consolidation.
Port Congestion and Its Impact on Delivery
Port congestion remains one of the biggest disruptors of efficient shipping:
U.S. West Coast ports like Long Beach and Los Angeles often face backlogs, delaying unloading and increasing overall cost and delivery time
Alternate ports with direct access to rail or trucking can speed up inland transport
Importers using busy ports during high-traffic periods may face unexpected demurrage fees and longer dwell times.
Freight Forwarder Expertise and Routing Strategies
Choosing an experienced freight forwarder makes a significant difference:
Forwarders have the ability to select different shipping routes based on cargo type, destination, and customs requirements
They offer insights into strategic shipping routes China uses, and optimize for transit performance or budget
Advanced logistics software also allows forwarders to calculate risk points, such as weather-related delays or geopolitical issues that might impact canal passages.
Route Type and Transport Infrastructure
There are multiple types of shipping paths:
Direct routes via the Pacific are shorter and faster but may face congestion
Panama Canal or Suez Canal paths are longer, but offer alternative entry points into the U.S. East Coast or Gulf Coast
Infrastructure at the destination port also affects delivery speed — ports with better warehousing and customs clearance zones process goods faster
The final selection depends on the balance between transit time, cost, and reliability.
East Coast vs. West Coast vs. Gulf Coast – Which is the Best Destination?
Destination?
When shipping goods from China to the United States, your choice of arrival region significantly affects transit time, shipping costs, and downstream logistics. Importers often compare the West Coast, East Coast, and Gulf Coast ports to decide the most efficient and cost-effective route based on product type, destination market, and urgency.
West Coast – Fastest Route with High Congestion Risk
The U.S. West Coast is the closest region to China via the Pacific Ocean, offering the shortest sea route and fastest shipping times:
Popular Ports: Los Angeles, Long Beach, Oakland, Seattle
Transit Time: ~14–20 days from China
Pros:
Quick access to California, Arizona, and Nevada
Ideal for urgent or high-volume shipments
Cons:
Frequent port congestion
Higher local handling fees
This is the preferred route for many, but rising volumes may cause delays — especially during peak seasons.
East Coast – Longer Route but Better Distribution Access
The East Coast is best accessed via the Panama Canal or Suez Canal, allowing direct shipping to ports like New York/New Jersey, Savannah, and Charleston:
Transit Time: ~25–35 days
Pros:
Closer to major markets like New York, Philadelphia, and Washington D.C.
Often less congested than the West Coast
Cons:
Longer east coast distance by sea
Canal transit fees may increase freight costs
It’s ideal for businesses targeting the Atlantic route or East Coast-based distribution centers.
Gulf Coast – A Balanced Option for Southern U.S. Delivery
Ports along the Gulf Coast — such as Houston and New Orleans — are rising in popularity due to strategic location and growing infrastructure:
Transit Time: ~28–38 days
Pros:
Central access to Texas, Louisiana, and surrounding regions
Less congested and often lower fees
Cons:
Not ideal for time-sensitive shipments
Limited rail connections in some terminals
As USA shipping routes diversify, Gulf Coast ports provide flexibility, especially for sea and land transport to the U.S. heartland.
How to Choose the Best Destination Port?
Your best choice depends on:
End market location in the U.S.
Required transit time
Product sensitivity to delay
Availability of customs and warehousing services
Many logistics providers now combine arrival ports with rail or truck freight, offering sea and land transportation solutions that reduce total lead time even if sea transit is longer.
Frequently Asked Questions about Shipping Routes from China to the USA
How far is China from the United States by sea?
The distance from China to the USA by sea varies depending on the route.
Shanghai to Los Angeles: ~6,000 nautical miles
Ningbo to New York (via Panama Canal): ~11,000 nautical miles
This translates into a sea route distance of approximately 14–35 days in transit time, depending on the destination port and route.
How long does shipping take from China to the US?
By Sea:
West Coast: 14–20 days
East Coast: 25–35 days
Gulf Coast: 28–38 days
By Air:
3–7 days, including customs clearance
Shipping time may vary due to port congestion, weather, or customs delays.
How far is China from America by air?
The air route distance between China and the United States is around 6,000–7,500 miles, depending on origin and destination airports. A direct flight from Shanghai to Los Angeles takes about 13 hours.
How far is China from the US in general terms?
Measured globally, China is approximately 7,000 miles away from the United States, depending on whether you measure city-to-city or port-to-port.
How far is the United States from China in nautical miles?
The distance between China and the United States ranges between 6,000 and 11,000 nautical miles, depending on port selection and chosen shipping lane (Pacific route vs. Panama Canal route).
How far is China to America by cargo ship?
Shipping from China to America via cargo ship takes between 2 to 5 weeks, based on final destination and route. Most cargo ships from China use the Pacific route to the West Coast or the Panama Canal route to the East Coast.
Can China ship to America directly?
Yes. China ships to the United States daily, both by sea freight and air freight. There are direct routes to major U.S. ports and airports, with thousands of containers and tons of air cargo departing from China every day.
What does ‘shipped from China’ mean in tracking updates?
This status indicates your package or cargo has left the origin port or airport in China and is en route to its destination — usually across the Pacific Ocean if headed to the U.S.
Conclusion – Choose the Optimal Route with a Reliable Freight Forwarder
Shipping from China to the USA involves more than simply choosing the shortest path — it’s about selecting the right shipping method, minimizing risk, and optimizing both transit time and shipping costs. With growing complexities in the international shipping landscape, including port congestion, fuel price fluctuations, and evolving trade policies, making informed decisions has never been more critical.
Whether you’re moving goods via sea freight, air freight, or a combined sea and land transportation model, partnering with an experienced freight forwarder ensures smoother operations and peace of mind. From booking vessels to managing customs documentation and route planning, your freight partner plays a vital role in navigating the global shipping industry.
Why Choose Tonlexing as Your China–USA Freight Partner?
At Tonlexing, we specialize in crafting tailored logistics solutions for businesses shipping from China to the United States. Our team of experts can:
Recommend the most cost-effective and reliable shipping routes
Offer competitive shipping costs for both air and ocean cargo
Ensure compliance with international trade regulations and customs requirements
Monitor and adapt to real-time changes across major routes like the Pacific Ocean, Panama Canal, and Atlantic trade lanes
Whether you’re shipping a single container or managing high-frequency orders, we provide scalable services to match your needs.
👉 Contact Tonlexing today to get a customized freight quote and optimize your route from China to the USA.

