Importing electronics from China has become a lucrative business opportunity for companies and individuals worldwide. China is the global leader in electronics manufacturing, producing everything from consumer gadgets and industrial equipment to automotive electronics and smart home devices at highly competitive prices.
However, the process of importing electronics involves choosing reliable suppliers, ensuring product compliance with regulations, calculating costs, and selecting the most efficient shipping method.
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to sourcing, importing, and shipping electronics from China, helping businesses optimize their supply chains while minimizing risks and costs.

Table of Contents
Introduction to Electronics Import from China
China is the world’s largest electronics manufacturing hub, producing a vast range of products, from consumer gadgets like smartphones, laptops, and smartwatches to industrial electronics such as circuit boards, power supplies, and automation systems. The country’s advanced production capabilities, efficient supply chains, and cost advantages make it the preferred destination for businesses and entrepreneurs looking to import electronics.
However, importing electronics fromChina to the USA requires careful planning. From choosing the right supplier and understanding legal requirements to calculating total costs and selecting the best shipping method, every step plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth delivery and compliance with U.S. regulations.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about importing electronics from China, including:
- How to find reliable electronics suppliers.
- Understanding product development and cost calculations.
- Navigating U.S. import regulations and certifications.
- Choosing the best shipping methods and estimating costs.
- Avoiding customs clearance issues and unexpected fees.
By following these steps, businesses can successfully import high-quality electronics while minimizing risks and maximizing profitability.
Sourcing Electronics from China
Not all electronics will yield high profits—some products may have high competition, import restrictions, or hidden costs. Before choosing a product, analyze these key factors:
Market Demand & Competition
Before selecting a product, analyze consumer demand and competition levels:
- Use Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba trends – Identify best-selling electronics.
- Check Google Trends – Track search interest over time.
- Analyze Competitor Pricing – Research how established brands price similar products.
- Look for Emerging Technologies – AI-powered, smart home, and health tech products are booming.
💡 Pro Tip: Avoid oversaturated markets—instead, focus on niche electronics with unique features.
Import Restrictions & Compliance
Certain electronic products must meet legal and safety standards before entering markets like the USA, EU, and Australia.
Common regulations & certifications for electronics imports:
- FCC (Federal Communications Commission, USA) – Required for all wireless and electronic devices.
- CE (European Conformity, EU) – Needed for electronics sold in European countries.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – Ensures electronics don’t contain harmful substances like lead or mercury.
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories, USA) – Certification for safe electrical products in North America.
- PSE (Product Safety Electrical Appliance & Material, Japan) – Mandatory for Japan-bound electronics.
💡 Pro Tip: If a supplier cannot provide certification documents, their products may fail customs clearance or be rejected from major retailers.
Shipping Costs & Logistics
Electronics are lightweight but can be fragile, requiring secure packaging and fast shipping.
- Small electronics (smartwatches, earbuds) – Use air freight for faster delivery.
- Bulkier electronics (TVs, gaming consoles) – Ship via sea freight for cost savings.
- Battery-powered devices (EV batteries, power banks) – Must comply with lithium battery shipping regulations.
💡 Pro Tip: Check if your product contains lithium batteries—many airlines restrict or charge extra for these shipments.
Customs Duties & Import Taxes
Different electronic products have different import tax rates based on the Harmonized System (HS) Code classification.
- USA: Most consumer electronics (smartphones, laptops, gaming consoles) have zero import duty, but home appliances and industrial electronics may be subject to 5%–25% tariffs.
- EU: Most electronics are subject to 0%–14% import duties, depending on classification.
- Middle East: Many countries like UAE and Saudi Arabia have a 5% standard import duty.
💡 Pro Tip: Always check the HS Code and duty rates before finalizing an electronics order.
Final Tips for Importing Electronics from China
- Choose niche products – Avoid highly competitive categories unless you can offer unique features or lower pricing.
- Verify supplier credentials – Ensure manufacturers have FCC, CE, or UL certifications.
- Factor in total costs – Include import duties, taxes, and shipping fees in the final pricing.
- Consider branding & private labeling – OEM or private-label products offer higher profit margins.
- Plan for safe shipping – Use shockproof packaging and work with freight forwarders experienced in electronics shipping.
Next Steps: Selecting a Reliable Supplier & Shipping Method
After choosing profitable electronics, the next step is to find a reliable supplier, calculate total import costs, and select the best shipping method for your business.

Choosing a Reliable Electronics Supplier in China
Selecting the right supplier is crucial to ensure product quality, compliance, and timely delivery. Importers can find electronics manufacturers through online platforms, trade fairs, and direct factory sourcing. However, verifying supplier credibility is essential to avoid low-quality products, fraudulent vendors, or shipping delays.
Where to Find Suppliers
China offers multiple sourcing channels for importing electronics. The best platforms and locations include:
B2B Online Marketplaces
- Alibaba – The largest wholesale platform, offering thousands of OEM & ODM electronics suppliers.
- Made-in-China – Verified manufacturers that specialize in export-grade electronics.
- Global Sources – Focuses on high-quality electronics factories with export experience.
💡 Best For: Businesses looking for bulk electronics orders with customization options.
Physical Electronics Markets in China
- Shenzhen Electronics Market – The world’s largest consumer electronics hub, with thousands of wholesalers and manufacturers.
- Guangzhou Huaqiangbei Market – A massive marketplace for smartphones, accessories, and components.
- Yiwu International Trade Market – Specializes in low-cost electronic accessories and gadgets.
💡 Best For: Buyers who want in-person supplier verification and direct price negotiations.
Trade Fairs & Exhibitions
- Canton Fair (Guangzhou) – China’s largest trade show, featuring a wide range of electronics manufacturers.
- Hong Kong Electronics Fair – A top global event showcasing cutting-edge tech and gadgets.
- CES Asia (Shanghai) – Focuses on high-tech and innovative consumer electronics.
💡 Best For: Importers looking to network with factory owners and discover new electronics trends.
How to Verify Supplier Credibility
Not all Chinese suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Before finalizing a purchase, conduct thorough due diligence:
Check Business Licenses & Company Background
- Request China’s Business License Number to verify the supplier’s registration.
- Use Alibaba’s Gold Supplier & Verified Supplier status to filter trustworthy manufacturers.
- Search on China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) to confirm legitimacy.
💡 Red Flags: Suppliers that refuse to provide business registration documents or have inconsistent company details.
Request Certifications for Electronics Imports
Different markets require specific certifications for importing electronics. Ensure the supplier provides:
- FCC (USA) – Required for wireless and electronic devices sold in the U.S.
- CE (EU) – Mandatory for electronics sold in European countries.
- RoHS (Global) – Ensures that electronics do not contain hazardous materials like lead or mercury.
- UL (North America) – Safety certification for electrical products in the U.S. and Canada.
💡 Red Flags: Suppliers that cannot provide compliance documents or send fake certificates.
Conduct Factory Audits & Third-Party Inspections
Before committing to a large electronics order, conduct a factory audit:
- Hire a third-party inspection service (e.g., SGS, TUV, Bureau Veritas) to verify the factory’s production capabilities.
- Check for proper manufacturing processes, employee working conditions, and quality control procedures.
- Inspect the supplier’s raw materials and components to ensure they meet industry standards.
💡 Red Flags: Suppliers who refuse on-site factory inspections or provide vague production details.
Order Product Samples Before Bulk Purchases
Never place a large order without testing the product. Before mass production:
- Request a sample unit to evaluate performance, build quality, and durability.
- Check product packaging & labeling to ensure it meets import compliance requirements.
- Compare multiple suppliers to find the best price-to-quality ratio.
💡 Red Flags: Suppliers who charge excessive sample fees or refuse to send product samples.
Final Checklist for Selecting a Trusted Electronics Supplier
✅ Verified business license & export experience.
✅ Compliance with FCC, CE, RoHS, and UL certifications.
✅ Positive trade history & customer reviews.
✅ Allows factory inspections & product sampling.
✅ Competitive pricing without hidden costs.
By following these steps, importers can avoid unreliable suppliers and ensure smooth electronics procurement from China.
Developing & Customizing Electronic Products from China
For businesses looking to stand out in the market, customizing electronic products is essential. China’s electronics manufacturers offer both OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) services, allowing importers to create unique branded products or modify existing designs to meet market demands.
OEM vs. ODM Production
Before selecting a supplier, businesses should understand the difference between OEM and ODM production models:
| Production Type | Definition | Best For | Example Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces electronics under your brand based on your designs and specifications. | Businesses with existing product concepts and designs looking for cost-effective mass production. | Branded smartphones, Bluetooth speakers, gaming accessories. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer provides pre-designed products, allowing for branding, minor modifications, and rebranding. | Importers who want ready-made products with minor modifications. | Smartwatches, wireless earbuds, smart home devices. |
💡 Tip: If your goal is to launch a unique electronic product, go with OEM production. If you want faster market entry with lower R&D costs, ODM is the better option.
Customization Options for Electronics
Chinese manufacturers provide a range of customization services to help businesses develop unique products:
Branding & Private Labeling
- Add custom logos, engraved branding, or silk-screen printing on devices.
- Customize product packaging, instruction manuals, and barcodes for retail.
- Include customized accessories (e.g., branded charging cables, carrying cases).
💡 Best For: Companies looking to sell under their own brand name with a professional retail presentation.
Hardware Modifications
- Adjust battery capacity for longer device usage.
- Upgrade screen resolution or display size for better visuals.
- Modify circuit board designs for enhanced processing power.
- Add new connectivity options (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, NFC, 5G).
💡 Best For: Businesses needing product differentiation with enhanced features.
Software Customization
- Develop custom firmware to modify device behavior.
- Create branded mobile apps for smart home, fitness, or IoT products.
- Localize language support for different global markets.
- Implement security & encryption features for sensitive devices.
💡 Best For: Businesses targeting tech-savvy consumers who demand unique software experiences.
How to Develop Custom Electronic Products in China
- Step 1: Define Your Product Requirements – Specify design, features, and target audience.
- Step 2: Choose OEM or ODM Production – Decide if you need custom manufacturing or pre-designed modification.
- Step 3: Verify Manufacturer Capabilities – Ensure the supplier can meet quality, safety, and compliance standards.
- Step 4: Request Prototypes & Samples – Test functionality before mass production.
- Step 5: Finalize Contracts & Manufacturing Agreements – Protect your intellectual property (IP) and ensure clear production terms.
Final Thoughts
Customizing electronic products through OEM and ODM manufacturing allows businesses to build unique brands and differentiate from competitors. By working with reliable Chinese suppliers, importers can develop high-quality, market-ready electronics at competitive costs.
Calculating the Cost of Importing Electronics from China
Importing electronics from China requires a clear understanding of all associated costs to ensure profitability. Beyond just the factory price, businesses must consider shipping fees, customs duties, quality control, and warehousing expenses.
This section provides an in-depth breakdown of cost components, estimated expenses for 2025, and how to calculate the Total Landed Cost (TLC) before making purchasing decisions.
Key Cost Factors in Electronics Importing
| Cost Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Cost | Wholesale price from the manufacturer (varies by product type). |
| Shipping Fees | Air, sea, or express freight from China to the USA. |
| Customs Duties & Taxes | Import tariffs based on HS code, FCC compliance fees. |
| Quality Control & Inspection | Pre-shipment testing to ensure product quality. |
| Warehousing & Storage | If using Amazon FBA, third-party logistics (3PL), or local storage. |
📌 Tip: Always calculate all costs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
Estimated Import Costs for Electronics (2025)
The final cost per unit depends on multiple factors, including the type of product, shipping method, and import duties. Below are estimated costs for 2025 based on common shipping methods:
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Product Cost (Factory Price) | $10 – $500 per unit (varies by electronics type). |
| Air Freight (Standard Shipping) | $4 – $7 per kg. |
| Express Air Freight (DHL/FedEx/UPS) | $6 – $12 per kg. |
| Sea Freight (FCL 40ft Container) | $3,500 – $5,000 (depending on the route). |
| Sea Freight (LCL per CBM) | $100 – $200 per cubic meter. |
| U.S. Import Duties & Taxes | 0% – 25% (based on HS Code). |
| FCC Certification (if required) | $1,500 – $5,000 per model. |
| UL & RoHS Compliance (if required) | $500 – $3,000 per product type. |
| Quality Inspection Fees | $200 – $400 per batch. |
| Amazon FBA Storage Fees (if applicable) | $0.63 – $1.40 per cubic foot/month. |
💡 Note: Prices fluctuate due to freight demand, regulatory changes, and peak seasons. Always request updated quotes from suppliers and freight forwarders.
How to Calculate Total Landed Cost (TLC)
To determine profitability, businesses must calculate the Total Landed Cost (TLC), which includes all expenses from manufacturing to delivery in the USA.
Formula for Total Landed Cost (TLC):
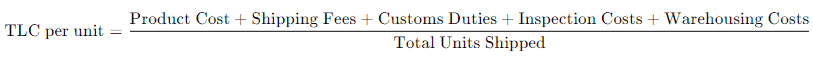
Example Calculation (Smartphone Import – 500 Units)
| Cost Component | Amount (USD) |
|---|---|
| Product Cost (Factory Price) | $150 per unit ($75,000 total). |
| Air Freight (500 kg at $6/kg) | $3,000 total. |
| Import Duties (10% on CIF value) | $7,800 total. |
| FCC Certification | $3,500 total. |
| Quality Inspection Fees | $500 total. |
| Amazon FBA Storage (2 months) | $1,200 total. |
| Total Cost (TLC for 500 units) | $91,000 |
| TLC per unit | $182 |
💡 Final Pricing Consideration: If selling the smartphone for $299 per unit, the profit margin per unit would be $117, excluding additional marketing, platform fees, or local distribution costs.
Tips to Lower Import Costs
- Negotiate with Suppliers – Bulk orders often receive better pricing.
- Choose Cost-Effective Shipping – Sea freight is cheaper for large shipments.
- Consolidate Shipments – Avoid multiple small shipments to reduce customs fees.
- Ensure Proper Documentation – Avoid customs delays and extra fees.
- Partner with a Reliable Freight Forwarder – Logistics experts like Tonlexing can optimize shipping routes and lower costs.
Final Thoughts
Calculating Total Landed Cost (TLC) ensures profitability and cost control in importing electronics from China. By understanding all cost components, businesses can choose the best logistics strategy, minimize expenses, and improve profit margins.
Legal Requirements & Documentation for Importing Electronics into the USA
When importing electronics from China to the U.S., businesses must comply with strict regulatory requirements, including product certifications, import documentation, and customs duties. Ensuring compliance prevents delays, customs seizures, or penalties.
This section provides an in-depth breakdown of required documents, U.S. import duties, and key regulatory requirements for electronic products.
Required Import Documents
To clear U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), importers must provide accurate and complete documentation:
| Document | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Commercial Invoice | Details product description, value, and seller information. |
| Packing List | Lists weight, dimensions, and packaging details. |
| Bill of Lading (BOL) / Airway Bill (AWB) | Acts as a shipping contract and proof of shipment. |
| Certificate of Origin (COO) | Required for duty exemptions under trade agreements. |
| Importer Security Filing (ISF – 10+2) | Required for ocean shipments before departure. |
| Customs Bond (For shipments over $2,500) | Required to cover potential duty payments. |
Tip: Incorrect or missing documents can lead to shipment delays or rejection at customs.
Compliance & Certifications for Electronic Products
Certain electronic products require mandatory safety and compliance certifications before they can be legally imported and sold in the U.S.
| Certification | Requirement |
|---|---|
| FCC Certification | Required for electronics emitting radio frequencies (e.g., smartphones, Wi-Fi devices, laptops). |
| UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Certification | Ensures product safety for electrical devices. |
| RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) | Confirms no hazardous materials (e.g., lead, mercury, cadmium). |
| CE Marking (If selling in the EU as well) | Compliance for electronics in the European market. |
Tip: Failure to meet FCC, UL, or RoHS standards can result in fines, product recalls, or shipment rejection at customs.
U.S. Import Duties & Tariffs on Electronics
Import tariffs on electronics vary based on the Harmonized System (HS) Code and trade regulations.
| Product Type | General Tariff Rate |
|---|---|
| Smartphones & Laptops | 0% (Duty-free under most HS codes). |
| Tablets & Wearables | 0% – 5%. |
| TVs & Monitors | 5% – 15%. |
| Electronic Components (PCBs, Batteries, IC Chips) | 0% – 25%. |
| Home Appliances (Microwaves, Refrigerators, etc.) | 2% – 10%. |
| Lighting & LED Products | 5% – 25%. |
Section 301 Tariffs (U.S.-China Trade War Tariffs)
Certain Chinese-made electronics face additional Section 301 tariffs of 7.5% – 25%. Importers must check if their product is affected.
De Minimis Rule for Duty-Free Imports
- Goods valued under $800 USD per shipment are duty-free under the De Minimis Rule.
- Applies mainly to small parcels sent via express couriers (DHL, FedEx, UPS).
- Bulk shipments exceeding $800 USD must pay import duties and processing fees.
Common Customs Fees & Taxes
In addition to import duties, businesses must pay additional fees upon entry to the U.S.:
| Fee Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF) | 0.3464% of the CIF value (Minimum: $29.66, Maximum: $575.35). |
| Harbor Maintenance Fee (HMF) – For Ocean Freight | 0.125% of the shipment value (not applicable to air freight). |
| Customs Broker Fee | $100 – $500 per shipment (optional, but recommended). |
Tip: Using DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) shipping transfers customs clearance responsibility to the seller, reducing delays.
How to Ensure Smooth Customs Clearance
- Classify Products Correctly – Use the correct HS Code to avoid misclassification penalties.
- Provide Accurate Documentation – Ensure all forms are complete and match invoice details.
- Work with a Licensed Customs Broker – They handle customs clearance and duty calculations.
- Consider DDP Shipping – Allows the supplier to prepay duties and taxes before arrival.
Setting Up Secure Payment Methods
Securing safe and reliable payment methods is crucial when importing electronics from China. Since electronics are high-value goods, buyers must protect their transactions from fraud and supplier disputes.
Common Payment Options
- Telegraphic Transfer (T/T): A direct bank transfer widely used for bulk orders. It is secure but has higher transaction fees and requires trust in the supplier.
- Alibaba Trade Assurance: A buyer-protection service available on Alibaba that allows disputes and refunds if suppliers fail to deliver as agreed. It is a safer option for first-time importers.
- PayPal & Credit Cards: Convenient for small orders and sample purchases, but fees can be higher (3–5%), and not all suppliers accept PayPal.
- Letter of Credit (L/C): A bank-backed payment method used for large-volume transactions (typically over $50,000). It is highly secure but involves a complex process and additional bank fees.
Best Payment Practices
To reduce financial risk, buyers should follow these best practices:
- Never pay 100% upfront. A common structure is a 30% deposit before production and 70% payment before shipment.
- Use escrow services or a third-party verification service when dealing with a new supplier.
- Request a Proforma Invoice to verify product details, terms, and payment schedules before making payments.
- Establish long-term relationships with trusted suppliers to negotiate better payment terms and lower transaction costs.
Choosing the Right Shipping Method from China to the USA
Electronics shipping requires speed, security, and cost-efficiency. Choosing the right method depends on shipment size, urgency, and budget.
Air Freight – Fastest Option for Electronics
Air freight is the preferred method for high-value, time-sensitive electronic shipments. It offers fast transit times but comes at a higher cost than sea freight.
- Standard Air Freight (5–8 days): Cost-effective for bulk shipments.
- Express Air Freight (2–5 days): Uses premium carriers like DHL, FedEx, and UPS for urgent deliveries.
- DDP Air Freight (6–12 days): Covers customs clearance, duties, and taxes for hassle-free delivery.
This method is best suited for smartphones, laptops, medical devices, and high-end consumer electronics.
Sea Freight – Best for Bulk Orders
For businesses importing large quantities of electronics, sea freight is the most cost-effective solution. Although it has a longer transit time, it allows companies to save on shipping costs.
- Full Container Load (FCL): Ideal for large shipments over 15 CBM, offering lower per-unit shipping costs.
- Less than Container Load (LCL): Best for smaller shipments (1–15 CBM), allowing businesses to share container space with other importers.
- DDP Sea Freight: A door-to-door shipping solution that includes customs duties and final delivery.
This method is best for larger consumer electronics, appliances, and industrial equipment.
Rail Freight – Alternative for U.S. Importers via Europe
Rail freight is an increasingly popular option for shipping electronics from China to the USA via Europe.
- Transit time: 14–25 days, which is faster than sea freight but cheaper than air freight.
- Lower carbon footprint compared to air freight.
- Best suited for medium-sized shipments of electronic components and consumer electronics.
Rail freight is particularly beneficial for companies shipping electronics in bulk to the U.S. through European distribution centers.

Best Practices for Importing Electronics from China
To ensure a smooth and efficient import process, businesses should follow these best practices:
- Order Product Samples: Always test products for quality, performance, and compliance before bulk purchasing.
- Work with a Freight Forwarder: Shipping electronics requires specialized handling. A freight forwarder can streamline logistics and avoid customs delays.
- Use Secure Payment Methods: Protect transactions using trade assurance, escrow services, and staged payments.
- Stay Updated on Regulations: Ensure all products comply with FCC, UL, and RoHS standards to avoid shipment rejection at U.S. customs.
- Monitor Supply Chain Risks: Work closely with suppliers to mitigate production delays, raw material shortages, and unexpected shipping disruptions.
Why Choose Tonlexing for Electronics Shipping?
Tonlexing specializes in electronics freight shipping from China to the USA, providing cost-effective, secure, and efficient logistics solutions.
- Expert Freight Services: Seamless air, sea, and rail freight shipping from China to the USA.
- Customs Clearance Assistance: Ensuring smooth and hassle-free import processing for high-value electronics.
- Competitive Rates: Transparent pricing with no hidden fees.
- Real-Time Tracking: Businesses can monitor shipments in real-time for added security and peace of mind.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) Shipping: Stress-free logistics with all-inclusive pricing covering duties, taxes, and last-mile delivery.
Get a Customized Shipping Solution
Importing electronics from China requires a trusted logistics partner. Tonlexing provides end-to-end shipping solutions tailored to your business needs.
📞 Contact Tonlexing today for a customized shipping quote and expert guidance on electronics imports from China!

