Reliable & Cost-Effective Shipping from China
Tailored Logistics Solutions for Your Business
- Home
- »
- Company News
- »
- Shipping from China to Asia
Shipping from China to Asia
- L. Liu
China has long been the powerhouse of manufacturing in Asia, supplying everything from electronics and textiles to machinery and raw materials. As trade within the Asia-Pacific region accelerates, shipping from China to Asia has become essential for businesses seeking on-time delivery, reduced costs, and fast market access.
With established logistics infrastructure, extensive port networks, and reliable international shipping options, China offers cost-effective solutions for importers across the region. Countries such as Japan, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, South Korea, and the Philippines rely heavily on freight services originating from key Chinese cities like Shanghai, Shenzhen, Ningbo, and Qingdao.
Whether you’re a growing business in Southeast Asia or a seasoned distributor in South Asia, understanding the available shipping methods, regional compliance requirements, and the right freight forwarder can help streamline your supply chain and enhance delivery performance.

Main Shipping Methods from China to Asia
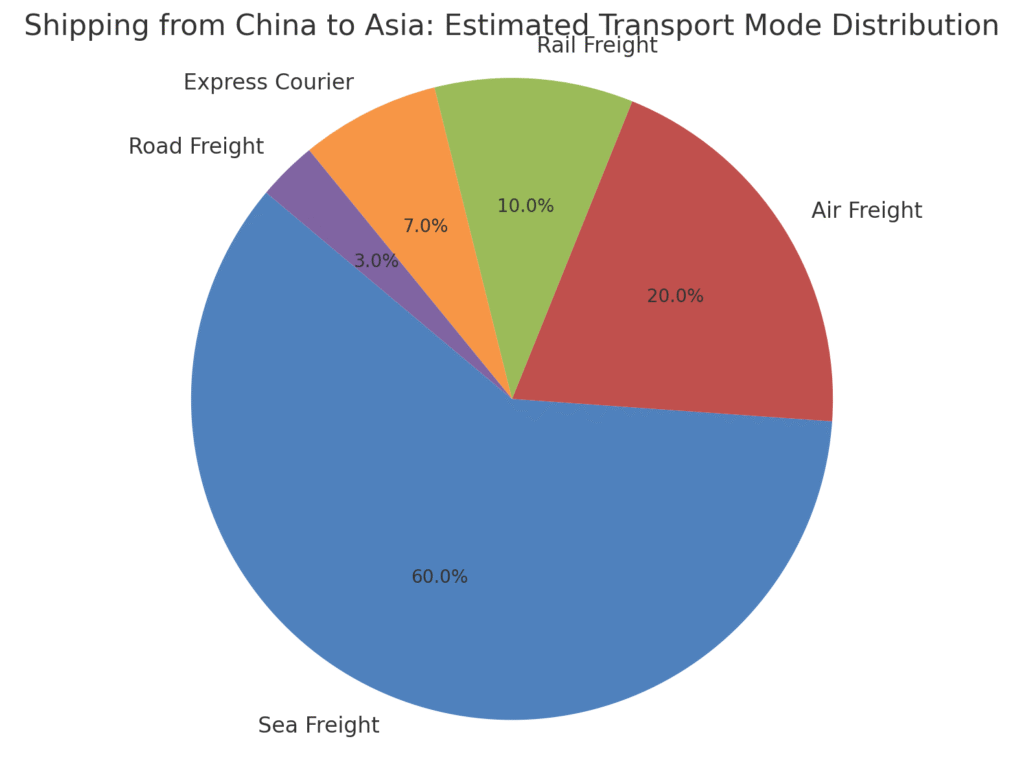
When shipping goods from China to other parts of Asia, choosing the right transportation method can significantly impact your delivery timeline, total cost, and cargo safety. The most common shipping services include sea freight, air freight, and rail freight, each with distinct advantages depending on cargo volume, urgency, and destination.
- Sea Freight remains the most economical option for bulk shipments. Ideal for both FCL (Full Container Load) and LCL (Less than Container Load), it’s widely used for heavy or non-urgent cargo bound for countries like Malaysia, Indonesia, and Vietnam.
- Air Freight is the fastest method, commonly chosen for high-value goods or tight deadlines. It offers direct routes to major cities like Bangkok, Manila, and Singapore with on-time delivery and reliable tracking systems.
- Rail Freight is increasingly used for overland shipments to Central and South Asia, including countries like Kazakhstan and Pakistan. It offers a good balance between cost and speed, especially for landlocked destinations.
Each method can be combined with door-to-door services, customs clearance, and cargo insurance for a full-service logistics experience.
Sea Freight: FCL & LCL Options for Asia-bound Cargo
Sea freight is the most widely used method for shipping from China to Asia, especially for businesses transporting large volumes of goods. It offers cost-effective pricing, regular sailing schedules, and the flexibility of both FCL (Full Container Load) and LCL (Less than Container Load) options.
- FCL shipping is ideal when you have enough cargo to fill an entire 20ft or 40ft container. It provides better security, faster handling at both ends, and lower cost per unit. It’s commonly used for shipments to ports like Singapore, Klang (Malaysia), Laem Chabang (Thailand), and Hai Phong (Vietnam).
- LCL shipping allows you to share container space with other shippers. This is a smart solution for small to medium-sized businesses or first-time importers with limited cargo volume. Although transit times can be slightly longer due to transshipment, it remains one of the most affordable solutions in international logistics.
Popular departure ports in China for sea freight include Shanghai, Shenzhen, Ningbo, and Qingdao, which offer well-established connections to major Asian trade hubs.
Air Freight from China to Asia: Fast and Reliable
When speed is a priority, air freight from China to Asia provides the fastest and most dependable option. It’s commonly used for high-value, time-sensitive, or perishable goods such as electronics, medical supplies, fashion items, and components for just-in-time production.
With access to world-class airports like Shanghai Pudong (PVG), Guangzhou Baiyun (CAN), and Beijing Capital (PEK), shippers can connect to major destinations across Asia including Tokyo, Seoul, Bangkok, Manila, Kuala Lumpur, and Jakarta—often via direct flights with on-time delivery guarantees.
While air freight is more expensive than sea or rail, it drastically reduces transit times, often delivering within 1–3 days. This makes it an ideal solution for urgent shipments and competitive e-commerce businesses that prioritize fast delivery across the Asia-Pacific region.
Most air shipping services also include cargo tracking, customs clearance, and door-to-door delivery, offering complete logistics support.
Rail Freight and Inland Transportation in Asia
For landlocked countries in Central and South Asia, such as Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and parts of India and Pakistan, rail freight and inland transportation are essential links in the China–Asia shipping network.
The China–Europe Railway Express and other cross-border railway routes now extend deeper into Asia, connecting inland logistics hubs like Xi’an, Chongqing, and Chengdu with Almaty, Lahore, and New Delhi. These services offer a balance between cost and speed, with transit times typically ranging from 12 to 20 days, faster than sea but cheaper than air.
Once rail containers arrive at inland depots or dry ports, trucking services take over to complete last-mile delivery, ensuring smooth inland distribution. For remote areas, rail and road integration provides a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution.
Inland shipping also supports multi-modal transportation, combining rail, truck, and sometimes sea freight to deliver goods across the continent with full cargo visibility and tracking.
Major Ports and Airports in China for Asian Shipping
China’s well-developed logistics infrastructure supports efficient shipping to every corner of Asia. Choosing the right port or airport for your cargo can optimize both transit time and shipping cost, depending on the destination and freight method.
Major Seaports
- Port of Shanghai: The busiest container port in the world, offering direct sailings to major Asian ports.
- Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan: Known for its extensive international routes and reliable container services.
- Port of Shenzhen: A key gateway for South China exports, close to Hong Kong and ideal for Southeast Asia routes.
- Port of Qingdao: Well-connected to North and Central Asia, including transshipment access to inland regions.
Major Airports
- Shanghai Pudong International Airport (PVG): Handles a high volume of air cargo bound for Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia.
- Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport (CAN): Preferred by e-commerce and express air freight clients due to its vast carrier network.
- Beijing Capital International Airport (PEK): Ideal for northern routes and cross-border express shipments.
These logistics hubs are fully equipped for customs inspection, cargo loading, VGMs, and compliance handling, ensuring smooth processing and minimized delays.
Popular Trade Routes and Transit Times
Understanding the most common shipping routes from China to Asia helps businesses plan better and meet delivery expectations. Transit times vary by destination and mode of transport, but many routes now offer fast and reliable options with minimal transshipment.
Sea Freight Routes
- Shanghai to Bangkok (Thailand): 6–9 days
- Ningbo to Manila (Philippines): 8–12 days
- Shenzhen to Ho Chi Minh City (Vietnam): 5–8 days
- Qingdao to Klang (Malaysia): 7–10 days
Air Freight Routes
- Shanghai to Tokyo: 1–2 days
- Guangzhou to Kuala Lumpur: 1–2 days
- Beijing to Seoul: 1 day
- Shenzhen to Jakarta: 2–3 days
Rail and Inland Routes
- Xi’an to Almaty (Kazakhstan): 12–14 days
- Chongqing to Lahore (Pakistan): 15–18 days
Choosing a direct route when possible reduces handling time and ensures on-time delivery. Many forwarders also offer guaranteed departure schedules, trackable shipments, and smart logistics planning to meet tight deadlines across the Asia-Pacific region.
Customs Clearance and Compliance Requirements
No matter which shipping method you choose, customs clearance is a crucial part of importing goods from China into other Asian countries. Each destination has its own regulations, import duties, and documentation requirements that must be strictly followed to avoid delays or penalties.
Key documents typically include:
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
- Bill of lading or air waybill
- Certificate of origin
- Product compliance certificates (if required)
To ensure smooth customs clearance, your shipment must meet local compliance standards, including product labeling, safety regulations, and any required licensing or pre-approvals—especially for food, electronics, or medical items.
Many Asian customs authorities now operate under electronic declaration systems, speeding up the process if documents are properly prepared and submitted. Partnering with a professional freight forwarder can help handle these procedures efficiently and ensure you meet all legal obligations.
Some countries also require VGM (Verified Gross Mass) submission before loading containers, a safety measure to ensure correct vessel balance and handling.
Shipping Costs and Rate Factors
Shipping costs from China to Asia can vary significantly based on several key factors, including the shipping method, cargo volume, destination, and seasonal demand. Understanding what influences your rate helps you plan better and avoid unexpected fees.
Key Factors Affecting Shipping Rates:
- Mode of Transport: Sea freight is generally cheaper than air freight or rail.
- Cargo Type and Volume: Heavier or bulky items cost more. LCL shipments often include handling and consolidation fees.
- Route Distance: Shorter routes like China to Vietnam are less expensive than longer routes to South Asia.
- Customs Duties and Taxes: Some countries impose higher import duties based on HS code and cargo value.
- Urgency and Delivery Time: Express or on-time delivery services come at a premium.
- Peak Season Surcharge: Rates increase during holidays like Chinese New Year and Q4 (October–December).
To get the most cost-effective solution, request quotes from multiple freight forwarders, and compare inclusive services such as door-to-door shipping, customs brokerage, tracking, and insurance.
Many shippers now use freight calculators and CBM tools to estimate total shipping expenses before placing orders.
Other country-specific shipping guides:
- Shipping from China to Japan
- Shipping from China to Korea
- Shipping from China to Malaysia
- Shipping from China to Philippines
- Shipping from China to Singapore
- Shipping from China to Vietnam
- Shipping from China to Thailand
- Shipping from China to Indonesia
- Shipping from China to India
- Shipping from China to Pakistan
Door-to-Door Services and Delivery Solutions
For businesses seeking simplicity and full-service logistics, door-to-door shipping from China to Asia is one of the most convenient options. This method covers the entire shipping process—from pickup at the supplier’s warehouse in China to final delivery at your destination address.
What’s Included in Door-to-Door Services:
- Domestic pickup from factory or warehouse
- Export customs clearance in China
- International shipping (by air, sea, or rail)
- Import customs clearance at the destination
- Inland delivery to your home, office, or warehouse
This integrated approach eliminates the need for multiple service providers and allows you to track your shipment from origin to destination. Whether you’re shipping to Thailand, the Philippines, Singapore, or India, door-to-door service ensures on-time delivery with full logistics support.
It’s particularly useful for small businesses, e-commerce sellers, and buyers unfamiliar with international shipping regulations. Many freight forwarders offer flexible plans tailored to different cargo sizes, deadlines, and budget requirements.
How to Choose a Freight Forwarder for Asia Shipping
Selecting the right freight forwarder is one of the most important decisions when managing international shipments from China to Asia. A reliable logistics partner ensures smooth customs clearance, timely pickups, and accurate tracking throughout the entire journey.
What to Look for in a Freight Forwarder:
- Experience in China–Asia routes: Choose forwarders with a strong network in both China and your destination country.
- Clear communication: They should provide updates, estimated transit times, and immediate support for any issues.
- Full-service offering: Look for providers who can handle sea freight, air freight, inland transport, warehousing, and door-to-door delivery.
- Competitive pricing: Rates should be transparent, with no hidden charges.
- Reliability and reputation: Read reviews, ask for references, and ensure they are known for on-time delivery.
A good forwarder helps you stay compliant with local regulations, avoids unnecessary delays, and keeps your clients satisfied through dependable shipping performance.
Conclusion: Efficient, Cost-Effective Transport to Asia
As China continues to lead global manufacturing and trade, its role in supplying goods across Asia becomes even more vital. Whether you’re shipping electronics to Japan, clothing to Malaysia, or industrial parts to India, understanding the right shipping methods, customs procedures, and logistics strategies is key to success.
With a variety of options—including sea freight, air freight, rail transport, and door-to-door delivery—you can choose the most suitable solution based on your timeline, cargo type, and budget. Working with an experienced freight forwarder ensures not only on-time delivery, but also full compliance, accurate documentation, and reliable tracking throughout your supply chain.
For importers and exporters across the Asia-Pacific region, shipping from China has never been more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective. If you’re ready to grow your business with reliable logistics, now is the time to take action—and partner with a shipping provider that understands your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best shipping method from China to Asia?
The best shipping method depends on your cargo type, urgency, and budget.
Sea freight is ideal for large or non-urgent shipments.
Air freight is fastest for time-sensitive goods.
Rail freight is suitable for inland destinations like Central or South Asia.
How long does it take to ship from China to Asia?
Transit times vary by country and shipping method:
Sea freight: 5–18 days
Air freight: 1–3 days
Rail freight: 12–20 days
Door-to-door delivery may take slightly longer depending on customs and inland transportation.
What are the customs requirements when shipping to Asia?
Most Asian countries require:
Commercial invoice
Packing list
Bill of lading or air waybill
Certificate of origin
Some destinations may also ask for compliance documents or licenses depending on the cargo type.
How much does it cost to ship goods from China to Asia?
Shipping costs depend on the mode (air, sea, rail), volume, weight, and destination.
Sea freight is the most cost-effective for bulk cargo.
Air freight is more expensive but much faster.
Always request an all-inclusive quote from a freight forwarder to understand total costs.
Can I use door-to-door service when shipping to Asia?
Yes. Many logistics providers offer full door-to-door services, which include pickup in China, international transport, customs clearance, and final delivery to your warehouse or customer address.

