DAP vs DDP: Customs Clearance, Import Duties, and Who Pays What
- Verified & Reviewed · Last updated January 2026
Choosing between DAP and DDP determines who handles import customs clearance, who pays import duties and taxes, and where cost risks may occur during international shipping.
This guide explains the practical differences between DAP and DDP under Incoterms® 2020 in clear, decision-focused language, helping importers and exporters choose the right term with confidence.
DAP vs DDP
Import Customs Clearance
Import Duties & Taxes

- Experienced China-based logistics specialists
Table of Contents
DAP vs DDP decision chart
Use this quick decision chart when quoting, negotiating, or choosing between DAP and DDP.
Choose DAP when
The buyer has a customs broker and understands customs clearance procedures
The buyer wants control over paying import duties and import taxes
The buyer’s country has strict importer rules that make it hard for the seller to act as importer
You want to reduce seller exposure to the import process and compliance risk
The buyer is responsible for a mature import program and can manage customs formalities efficiently
Choose DAP when
The buyer wants a simple process and a predictable landed cost
You ship to smaller importers, end customers, or e commerce buyers
You can support compliant import customs clearance in the destination country
You want fewer delivery surprises at the final destination
You offer ddp shipping services and have proven partners to manage duties and taxes
If you are not sure
Start with DAP and offer an option to upgrade to DDP after confirming compliance, duty estimation, and importer structure. This reduces disputes and protects both seller and buyer.
DAP vs DDP comparison table
| Topic | DAP Delivered at Place | DDP Delivered Duty Paid |
|---|---|---|
| Import clearance | Buyer handles import clearance | Seller is responsible for import clearance |
| Customs clearance | Buyer manages customs clearance procedures | Seller handles customs clearance procedures |
| Import duties and import taxes | Buyer pays import duties and import taxes | Seller pays import duties and import taxes |
| Export clearance | Seller usually completes export clearance | Seller usually completes export clearance |
| Risk transfers | When goods arrive ready for unloading | After import customs clearance, at delivery |
| Best for | Buyers with broker and import capability | Buyers who want predictable landed costs |
| Typical issue | Buyer delays create storage costs | Seller faces compliance and duty risk |
| Practical note | Works well for B2B importers | Works well for door to door and e commerce |
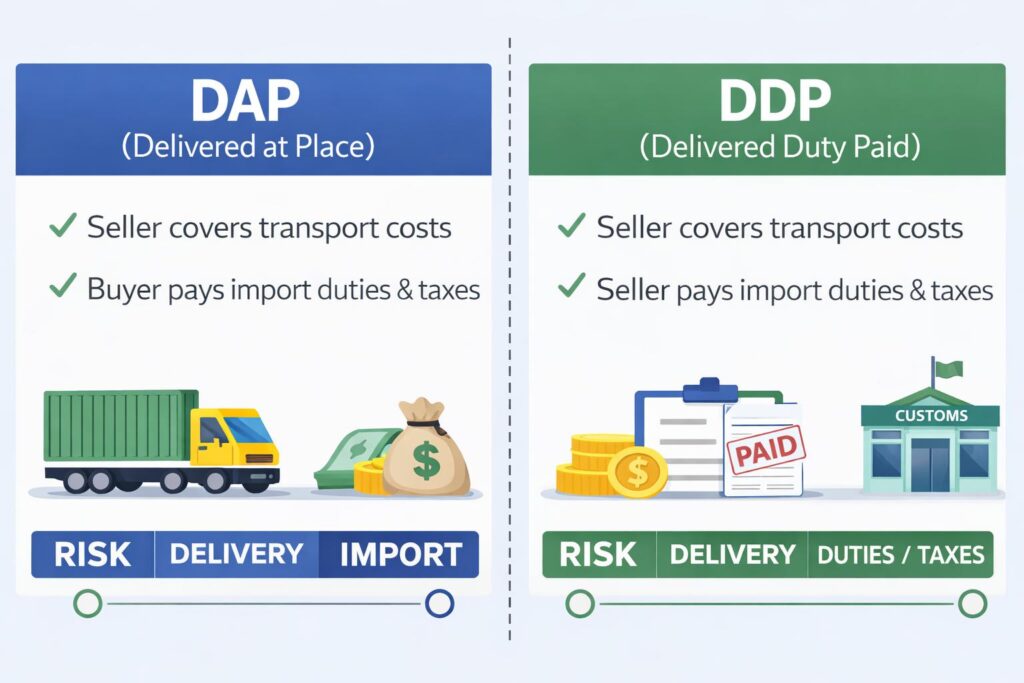
What DAP Delivered at Place means
DAP Delivered at Place means the seller delivers goods to the named delivery location in the destination country, ready for unloading. The delivery location can be the buyer’s premises, the buyer’s location at a warehouse, a port gate, or any agreed place.
With dap shipping, the seller often arranges main transport and export clearance. Once the goods arrive and are available for unloading, risk transfers to the buyer. After that moment, the buyer handles import clearance and import customs clearance.
Seller’s responsibilities under DAP
Seller’s responsibilities commonly include:
Export clearance and origin customs formalities
Main transport booking and coordination
Transportation costs and shipping related expenses to the delivery location
Seller delivers goods to the named place at the final destination, ready for unloading
Providing correct documents that support import procedures
In simple terms, the seller delivers to the place, but the buyer clears the border.
Buyer’s responsibilities under DAP
Under DAP, buyer assumes responsibility for:
Import clearance process and import formalities
Import customs clearance and handling customs clearance with a customs broker
Paying import duties, customs duties, duties and taxes, and import fees
Any storage, inspection, or local charges caused by delays
Compliance steps required in the destination country
This is why DAP is popular when the buyer has experience and wants control.
What DDP Delivered Duty Paid means
DDP Delivered Duty Paid means the seller takes maximum responsibility up to delivery at the buyer’s location. Many companies label it as ddp delivered duty paid, or ddp delivered duty paid on invoices to avoid confusion.
Under delivered duty paid, the seller is responsible for import customs clearance and for paying import duties and import taxes in the destination country. The buyer typically receives the cargo and manages unloading.
In practice, ddp shipping services require careful structure. Some countries restrict who can act as importer. If the seller cannot legally import, DDP may need an alternative structure, or the deal should move to DAP.
Seller’s responsibilities under DDP
Seller’s responsibilities under DDP often include:
Export clearance
Main transport, destination handling, and the delivery process to the final destination
Import clearance and customs clearance procedures
Paying import duties, import duties taxes, and import taxes
Paying import fees and customs fees required for release
Managing associated costs tied to customs procedures
DDP means the seller bears more financial responsibility and more operational responsibility.
Buyer’s responsibilities under DDP
Even with duty paid ddp, the buyer still needs to:
Provide accurate consignee and delivery location information
Be available for delivery appointments and the unloading process
Support compliance questions if products require extra documents
Avoid actions that create redelivery or extra handling charges
DDP reduces buyer’s involvement, but it does not eliminate cooperation.
Customs clearance and import clearance responsibilities
This section targets the highest intent searches around customs clearance, import customs clearance, import clearance, and handling customs clearance.a
Under DAP
The buyer handles import clearance
The buyer manages import customs clearance and customs formalities
A customs broker usually completes the import clearance process
The buyer pays import duties and import taxes as part of the import process
If the buyer is not prepared, the shipment can be held, causing customs fees, storage, and unexpected costs.
Under DDP
The seller is responsible for import clearance
The seller handles customs clearance procedures and import procedures
The seller pays duty charges, import fees, and duties and taxes
The seller manages the import process and bears most related delays
DDP is simpler for the buyer, but it is heavier on the seller. DDP works best when the seller has reliable partners in the destination country.
Import duties, import taxes, import fees, and associated costs
Import duties and import taxes drive most landed cost differences between dap and ddp. Import duties taxes may change based on HS code, declared value, and product restrictions.
Under DAP
The buyer pays import duties and import taxes. The buyer should confirm:
HS code and valuation method in the buyer’s country
Payment process for paying import duties
Import clearance process timing and documents
Local import procedures and any product approvals
Because the buyer pays, the buyer assumes responsibility for duty accuracy. A broker can help, but the buyer is responsible for final compliance.
Under DDP
The seller pays import duties and import taxes. The seller should prepare:
A duty estimate method and a buffer for changes
A clear scope of what is included, especially customs duties and import fees
A plan for inspections and document corrections
A control process to avoid compliance mistakes
Unexpected costs to watch
Unexpected costs often appear during customs clearance procedures:
Storage and demurrage at terminal
Inspection fees and extra handling
Document correction fees
Re classification and value adjustments
Redelivery and appointment costs at the buyer’s premises
To reduce unexpected costs, define who pays them in sales contracts.
Shipping costs and transportation costs breakdown
Shipping costs and transportation costs include more than the freight itself.
Under DAP
Seller bears main shipping costs to the named place
Buyer pays import side charges such as customs duties and import fees
Buyer pays duties and taxes after arrival
Buyer bears costs caused by delayed import clearance
Under DDP
Seller bears shipping costs plus import side costs
Seller pays import duties taxes and import fees
Seller bears more associated costs during customs procedures
Cost breakdown template
You can use this list on quote pages to explain the shipping process:
Origin charges and export clearance
Main freight and shipping fees
Destination handling charges
Customs broker fee and handling customs clearance
Import duties and import taxes
Final delivery to the buyer’s location
Risk transfers and risk management
Risk transfers defines when the risk moves from seller to buyer. Risk transfers is a key differences topic in ddp and dap disputes.
Risk transfers under DAP
Risk transfers when goods arrive at the delivery location ready for unloading. Once risk transfers, buyer’s risk includes delays related to customs clearance and the import clearance process.
Risk transfers under DDP
Risk transfers after import clearance is completed and the goods are delivered to the final destination ready for unloading. This reduces buyer’s risk during the border stage.
Practical risk management tips
Confirm document accuracy before departure
Set a deadline for document approval
Agree who pays storage if customs holds the shipment
Decide how to handle inspections and extra handling
Use a responsibility checklist to avoid confusion
International shipping process step by step
Many readers search for the international shipping process because they want a clear flow. This section improves time on page and helps rank for international shipping process and global shipping.
Step 1: Sales contract and Incoterm selection
Set the Incoterm and name the delivery location. Decide whether it is DAP or DDP, then define the final destination clearly.
Step 2: Export clearance and origin preparation
The seller usually completes export clearance. The seller delivers documents, confirms packing lists, and prepares the shipment for departure.
Step 3: Main transport and freight forwarders
The seller arranges transport through freight forwarders. Freight forwarders coordinate booking, loading, and tracking.
Step 4: Arrival and destination handling
After arrival, the shipment enters destination handling. This stage can create shipping related expenses if the cargo waits too long.
Step 5: Customs clearance and import clearance process
This stage is the most sensitive. Customs clearance procedures and customs formalities determine whether goods move quickly or get held.
Under DAP, buyer handles import clearance.
Under DDP, seller is responsible for import clearance.
Step 6: Delivery to the named place
After customs release, delivery continues to the buyer’s location. The delivery process ends when the goods arrive ready for unloading.
How freight forwarders handle DAP and DDP
Freight forwarders play a major role in the shipping process, but their scope depends on what the buyer and seller agree.
DAP with freight forwarders
In dap shipping, freight forwarders often manage transport and destination delivery, while the buyer’s broker manages import customs clearance. This split requires strong coordination.
DDP with freight forwarders
In ddp shipping, freight forwarders may coordinate the entire chain including handling customs clearance and final delivery. This often feels smoother for buyers because one party manages more steps.
Quote clarity that improves conversion
Ask freight forwarders to separate:
Transportation costs and shipping fees
Customs broker and handling customs clearance fees
Import duties taxes and import taxes
Local delivery and appointment fees
This reduces confusion about all the costs and financial responsibility.
How to write DAP and DDP correctly in sales contracts
Most disputes come from vague wording. A strong contract uses clear terms and a precise named place.
Write the named place clearly
Use a complete delivery location with city and address when possible. This reduces disagreements about the final destination.
Define who pays what
Even if DDP is used, specify what is included:
Duties and taxes included or excluded
Customs fees included or excluded
Storage and inspection handling
Appointment and redelivery handling
Add a simple delay clause
If customs selects the shipment for inspection, specify whether the seller bears those costs or whether they are shared. This prevents arguments and reduces unexpected costs.
Copy and paste responsibility checklist
DAP checklist
Seller’s responsibilities
Export clearance completed
Seller arranges transport and delivery to the delivery location
Seller delivers goods ready for unloading
Seller provides correct shipping documents
Buyer’s responsibilities
Buyer handles import clearance
Buyer handles import customs clearance and customs formalities
Buyer pays import duties and import taxes
Buyer manages customs broker
Buyer assumes responsibility after risk transfers
DDP checklist
Seller’s responsibilities
Export clearance completed
Seller arranges transport, destination handling, and delivery process
Seller is responsible for import customs clearance
Seller pays duty charges, import duties taxes, and import taxes
Seller bears most associated costs until delivery
Buyer’s responsibilities
Provide accurate delivery location and contact
Receive goods at the final destination
Manage unloading process
Common mistakes that increase unexpected costs
Mistake 1: unclear delivery location
A vague named place leads to disputes at the final destination. Always define the delivery location.
Mistake 2: assuming DDP is always possible
In some destination country markets, the seller cannot easily complete import formalities. Confirm structure before offering ddp delivered duty paid.
Mistake 3: ignoring customs delays
Customs clearance procedures can trigger inspections. Decide who pays storage, inspection fees, and extra handling.
Mistake 4: mixing responsibility
If both parties assume the other side is handling customs, the shipment stalls. Use checklists to keep the import process clear.
Use cases by business model and shipping mode
This section helps you outrank competitors by covering more search intent.
DAP vs DDP for e commerce buyers
DDP often improves the buyer experience because buyers do not face surprise duty payments at delivery. This can reduce refusals and improve conversion.
DAP can still work if the buyer is an experienced importer and wants control over paying import duties.
DAP vs DDP for B2B international trade
B2B importers often prefer DAP because they already have a customs broker and can handle import clearance procedures. They may also want to manage duties and taxes for accounting reasons.
DAP vs DDP for air freight
Air freight is fast, but customs can still cause delays. DDP can reduce buyer’s involvement. DAP can be cost effective when the buyer can clear quickly.
DAP vs DDP for ocean freight
Ocean freight involves more terminal time, so customs delays can be expensive. If the buyer delays import clearance, storage and demurrage can rise. In these cases, clarity on customs formalities and financial responsibility is critical.
Frequently Asked Questions
DAP means the buyer handles import clearance and pays import duties and import taxes. DDP means the seller is responsible for import clearance and paying import duties and taxes.
Under DAP, the buyer handles customs clearance and works with a customs broker in the destination country.
In most cases, the seller arranges main transport to the delivery location, while the buyer pays import duties, import taxes, and import fees.
DDP is commonly used as door to door because the seller handles import clearance and duty payment up to the buyer’s location.
Risk transfers under DAP at delivery ready for unloading. Risk transfers under DDP after import customs clearance at the final destination.
Related Incoterms & DDP Shipping Guides
Get a DAP or DDP Shipping Quote from China
Compare DAP vs DDP landed cost before you ship
Clear breakdown: freight, clearance, duties & taxes
China-based team for door-to-door options
Send your cargo details and destination — we’ll quote both options and recommend the right term.

